Caffeine (IH)
Caffeine (IH), with the molecular formula C₈H₁₀N₄O₂, is a naturally occurring alkaloid found in coffee, tea, and cocoa. It acts as a central nervous system stimulant, reducing fatigue and increasing alertness. Caffeine is widely used in pharmaceuticals, energy products, and dietary supplements. It is identified by the CAS number 58-08-2.
Molecular Structure:
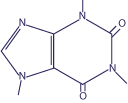
-
Molecular Formula: C₈H₁₀N₄O₂
-
CAS No. : 58-08-2
-
Categories : Caffeine is used in stimulants, analgesic adjuvants, dietary supplements, and pharmaceuticals.